How Do Brita Filters Compare to Other Water Filtration Methods?
Brita filters are a popular and affordable way to improve the smell and taste of tap water by reducing harmful contaminants like chlorine, lead, and mercury. However, they do have limitations compared to other water filtration methods, especially compared to the reverse osmosis systems. In this article, we will have a general idea about the capabilities of Brita filters, their key limitations, and how they stack up against alternative filtration methods.

High-Level Capabilities of Brita Filters
Brita filters are certified under NSF/ANSI Standards 42 and 53, which means they meet standards for reducing aesthetic impurities (like chlorine taste and odour) as well as specific health-related contaminants. Brita filters excel at improving water quality in several key areas:
- Chlorine Removal: Brita filters are highly effective at removing up to 99% of chlorine taste and odour from tap water. They use activated carbon, which acts like a sponge to trap chlorine and other impurities.
- Lead Reduction: Brita’s Elite Filter can remove up to 99% of lead, reducing it to safe drinking levels, as supported by research and EPA guidelines.
- Mercury Reduction: Brita filters also reduce mercury levels in water, ensuring compliance with safe drinking standards.
- Trace Metal Removal: Brita filters contain an ion-exchange resin, which helps reduce trace amounts of contaminants like zinc, copper, and cadmium.
Key Features of Brita Filters:
- Use activated carbon filtration to trap impurities like a sieve.
- Effectively remove chlorine taste and odour, lead, and mercury.
- Filter trace metals, such as zinc and copper, to safe levels.
It is worth noting that while Brita filters reduce specific contaminants effectively, their performance can vary depending on the specific filter model type and feed water quality.
Key Limitations of Brita Filters Regarding Water Hardness
One of the main limitations of Brita filters is their inability to soften water effectively. While Brita filters can remove temporary water hardness caused by calcium bicarbonate, they cannot address permanent hardness caused by calcium sulfate.
Why This Matters:
- Hard water minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, can build up in the filter over time and potentially leak back into the water if the filter is not replaced frequently.
- If you live in an area with hard water, a dedicated water softener will still be necessary to address these issues, even if you use a Brita filter.
Brita Filter FAQ
How Do Brita Filters Work?
Brita filters use a coconut-based activated carbon filter that acts like a sieve to catch and store particles. Additionally, they contain an ion-exchange resin that helps filter trace amounts of zinc, copper, and cadmium.
What Contaminants Do Brita Filters Remove?
Brita filters are certified under NSF/ANSI Standards 42 and 53, meaning they effectively reduce:
- Chlorine (taste and odour)
- Lead
- Mercury
- Some trace metals (e.g., zinc, copper, cadmium)
What Contaminants Do Brita Filters Not Remove?
Despite their effectiveness for specific contaminants, Brita filters do not remove the following:
- Fluoride
- Permanent water hardness (calcium sulfate)
- Other contaminants, including:
- Cadmium
- Benzene
- Asbestos
- Copper
- Zinc
- Pesticides/herbicides
How Often Should I Replace My Brita Filter?
- Standard Brita Filters: Replace every two months.
- Elite Filters: Replace every six months.
Failing to replace filters on schedule can result in contaminant buildup and reduced filtration effectiveness.
Why Might Filtered Water Have a Higher Bacteria Count Than Tap Water?
While Brita filters reduce certain dangerous organisms, they do not eliminate bacteria. Over time, the filter itself can become a breeding ground for bacteria as well as microorganisms if not replaced or maintained correctly.
Brita Filters vs. Reverse Osmosis Systems
If you are concerned that Brita filters only can effectively improve the taste and quality of water but you need more purification then you should look for reverse osmosis (RO) systems, which are more comprehensive. Here is a quick comparison below:
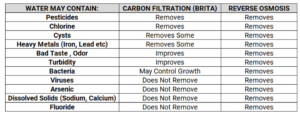
Summary:
- Brita filters are ideal for improving taste and odour and reducing common contaminants like chlorine and lead.
- Reverse osmosis systems are more comprehensive, removing a wider range of contaminants, including fluoride, bacteria, and dissolved solids.
Brita filters are a cost-effective and convenient solution for improving the taste and quality of tap water. Brita can effectively reduce chlorine, lead, and mercury, making them a reliable choice for many households. Understanding both the strengths and limitations of Brita filters can help you make an informed choise about the proper water filtration solution for your needs either its basic or advanced .
Leave a Reply